Across industries, there is an immense focus on streamlining last-mile delivery of services. Be it in Transportation or E-Commerce, hospitality or FMCG – industries have found a new mojo with ease-of-operation of last-mile delivery. The Telecom industry is going through a similar phase of transition i.e how do you effectively (from the perspective of capex, opex, agility, seamless operation & ease-of-use) connect consumers to services? This is gaining further importance now because of the expectation that 5G will bring a lot of new revenue-generating services. While every operator is rightly focusing on the spectrum bands & RAN, the way these are connected to the backbone network will have an immense impact on the competitiveness of the service provider. If one looks at the model of some recent greenfield operators, they are running their networks at very low cost-per-bit & hence are fiercely competitive while being profitable at the same time.
While 5G services are still in experimental/early phases & have a large dependency on country guidelines/regulations as well, it’s important to upgrade the transport architecture so that it doesn’t become a bottleneck towards competitiveness and profitability. Below are some of the technology and business considerations (however obvious they may sound) which an operator and vendor should pay attention to.
Technology Consideration: There are a myriad of technology options being promoted by different vendors depending on their legacy, however, the key theme should be around making the networks uniform / controllable from NOC & providing full control so that services have no dependency on the underlying infrastructure. Following will be a critical consideration in achieving those objectives:
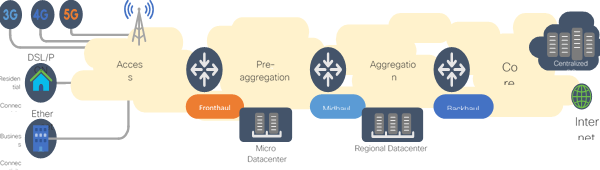
- Layer 1: The RAN network currently is predominantly using Microwave for layer 1 connectivity. Considering the Bandwidth/reliability & latency required, microwave technology is getting stretched. Fiber on the other hand does not have this limitation and is clearly the technology of choice.
- Layer 2: Over the years, most of the existing providers have built access networks that are running over different technologies (ATM, Frame-Relay, PPP, OTN etc). It’s evident that all these legacy technologies will converge over Ethernet. While Passive Ethernet is predominant in the wireline network, Active ethernet is going to play a huge role in the Mobile backhaul scenarios.
- Layer 3: Most importantly, Layer 3 functions will get extended to access networks. Moving IP to access enables Telcos to better, visualize, control & monetize their networks across a myriad of services. An increasing number of Telcos are building Cell Site Routers Instead of basic switches used earlier. Convergence over the IP network is inevitable.
- Services: Converged Services has to be the key behind any network upgrades. Network build-outs should be able to support any service from any point of the network. An ideal converged network will look like IP closer to users, backhaul over Active Ethernet with fiber underlay. The services of such a network will be easily extracted to the automation layer.
- Security: The number of last-mile access devices in the network will increase exponentially — and so will the entry points for security attack The attacks are getting increasingly sophisticated and with the high volume of devices connecting to the network – the risks of attack are higher than ever. One key area of consideration will be Device Security – which deals with tampering with devices, either the Software or Hardware.
An excellent white paper covering all the above-listed points can be found here: Converged 5G xHaul Transport
Read more about Technical Case Studies here: 5G Transport Case Studies
Business Consideration: As the next generation service is expected to evolve with 5G, the investment required on handset/ Spectrum / RAN / Network transport & application is going to be huge & staggered over several years. During such disruptive times, it is critical to choose the vendor partners from long-term perspective.
- Investment in Innovation: The scope of innovation in 5G space is massive and it will happen over several years as different ecosystem players come together. Hence, it is critical to partner with vendors who have the financial strength to continuously invest in innovation.
- Consumer and Business convergence: 5G services will enable the providers to deliver both residential and enterprise-class services via the same network. Hence, it will be critical to partner with vendors who have a strong and successful portfolio across both classes of services.
- Financial viability: 5G network and associated services will be developed over several years. There will be several technology/business decision which will iterate multiple times and mature over several years. It will be prudent and critical to partner with financial strong vendors for achieving the desired business outcome.
More information on Cisco’s products and Case Studies:
Sprint Strengthens Its IP Mobile Network for 5G with Cisco

CONNECT WITH US